hair restoration surgery
What is hair restoration surgery?
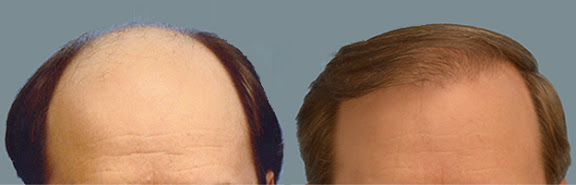
A hair restoration Surgery is a procedure in which a plastic or dermatological surgeon moves hair to a head's bald area. The surgeon usually moves hair from the head's back or side to the head's front or top. Hair restoration Surgery typically occurs in a medical office under local anesthesia.
Pattern baldness is liable for the bulk of hair loss. This comes down to genetics. The remaining cases are due to a variety of factors, including:
diet
stress
illness
hormonal imbalance
medications
Are there different types of hair restoration surgery?
There are two types of hair restoration Surgery procedures: slit grafts and micrografts.
Slit grafts contain 4 to 10 hairs per graft. Micrografts have 1 to 2 inches per graft, depending on the amount of coverage needed.
Who might benefit from a hair restoration surgery?
Receiving a hair transplant can improve your appearance and self-confidence. Good candidates for a hair transplant include:
men with male pattern baldness
women with thinning hair
anyone who has lost some hair from a burn or scalp injury
Hair replacement isn't a good option for:
women with a widespread pattern of hair loss throughout the scalp
people who do not have enough "donor" hair sites from which to get rid of hair for transplant
people who form keloid scars (thick, fibrous scars) after injury or surgery
people whose hair loss is due to a medication such as chemotherapy
What happens during a hair restoration surgery?
After thoroughly cleaning your scalp, a surgeon uses a little needle to numb a neighbourhood of your head with local anaesthesia.
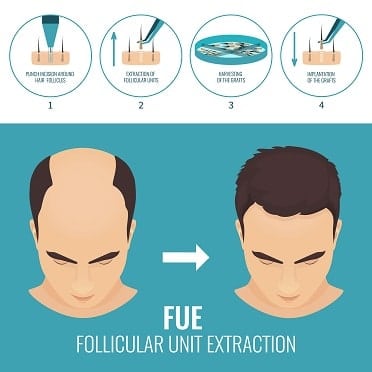
Two main techniques are wont to obtain follicles for transplantation:
FUT and FUE.
In follicular unit transplantation (FUT):
The surgeon will use a scalpel to chop out a strip of scalp skin from the top's rear. The incision is typically several inches long.
This is then closed with stitches.
Next, the surgeon separates the removed portion of the scalp into small sections using a magnifying lens and sharp surgical knife. When implanted, these sections will help achieve natural-looking hair growth.
In follicular unit extraction (FUE) the hair follicles are cut out directly from the rear of the top through hundreds to thousands of small punch incisions.
The surgeon makes tiny holes with a blade or needle in your scalp area receiving the hair transplant. They gently place hairs in these holes.
During one treatment session, a surgeon may transplant hundreds or maybe thousands of hairs.
After, the graft, gauze, or bandages will cover your scalp for a few days.
A hair transplant session can take four hours or more. Your stitches are going to be removed about 10 days after surgery.
You may require up to 3 or four sessions to realize the complete head of hair you desire. Sessions occur several months apart to allow each transplant to heal fully.
What happens after a hair restoration surgery?
Your scalp could also be sore, and you'll get to take medications following hair transplant surgery, such as:
pain medication
antibiotics to reduce your risk of infection
anti-inflammatory drugs to keep swelling down
Most people can return to figure several days after surgery.
It's normal for the transplanted hair to fall out two to 3 weeks after the procedure. This makes way for new hair growth. Most people will see some amount of latest hair growth 8 to 12 months after surgery.
Many doctors prescribe minoxidil (Rogaine) or the hair growth medication finasteride (Propecia) to enhance hair regrowth. These medications also help slow or stop future hair loss.
What are the complications associated with hair restoration surgery?
Side effects from a hair restoration Surgery are usually minor and clear up within a few weeks.
They can include:
bleeding
infection
swelling of the scalp
bruising around the eyes
a crust that forms on the areas of the scalp where hair was removed or implanted
numbness or lack of sensation on the treated areas of the scalp
itching
inflammation or infection of the hair follicles, which is understood as folliculitis
shock loss, or sudden but typically temporary loss of the transplanted hair
unnatural-looking tufts of hair
What is the long-term outlook?
Typically, people who've had a hair restoration Surgery will continue to grow hair in the scalp's transplanted areas.
The new hair may appear more or less dense depending on:
scalp laxity, or how loose your scalp skin is
the density of follicles in the transplanted zone
hair calibre or quality
hair curl
Suppose you don't take medication (such as minoxidil or finasteride) or undergo a low laser therapy level. In that case, you may continue to experience hair loss in nontreated areas of your scalp.


Comments
Post a Comment