scalp hair transplant
scalp hair transplant
Scalp Hair transplants are done to feature more hair to a neighbourhood on your head, thinning or balding. It's done by taking hair from thicker parts of the scalp or other parts of the body and grafting it to the scalp's thinning or balding section.
Worldwide, about 60 per cent of men and 50 per cent of women trusted Source experience some form of hair loss. To address this, people often use over-the-counter products, including topical treatments like minoxidil (Rogaine).
Hair transplant is another restoration method. The first transplant was performed in 1939 in Japan with single scalp hairs. In the following decades, physicians developed the "plug" technique. This involves transplanting large tufts of hair.
Over time, surgeons began using mini- and micro-grafts to minimize transplanted hair's appearance on the scalp.
Do scalp hair transplants work?
Scalp Hair transplants are typically more successful than over-the-counter hair restoration products. But there are some factors to consider:
Anywhere from 10 to 80 per cent of transplanted hairTrusted Source will fully grow back in an estimated three to four months.
Like regular hair, the transplanted hair will thin over time.
People with dormant hair follicles (sacs that sometimes contain hair beneath the skin but not grow hair) may have less effective transplants. Still, a plasma therapy can help up to 75 per cent or more of the transplanted hairs fully grow back.
Scalp Hair transplants don't work for everyone. They're mainly wont to restore hair if you're balding or thinning naturally or have lost hair thanks to an injury.
Most transplants are through with your existing hair, so they are not as useful for treating people with:
widespread thinning and baldness
hair loss due to chemotherapy or other medications
thick scalp scars from injuries
How much do scalp hair transplants cost?
Scalp Hair transplants can range from about $4,000 to $15,000 per session.
Final costs may depend on the:
the extent of the transplant procedure
availability of surgeons in your area
experience of the surgeon
surgical technique chosen
Because hair transplants are cosmetic procedures, health insurance won't pay for the course.
Aftercare medications can also increase the ultimate cost.
How does a hair transplant work?
Simply put, a hair transplant takes hair you've got and transfers it to a neighbourhood where you do not have hair. It's typically taken from the back of your head, but can also be taken from other parts of your body.
Before starting a Scalp hair transplant, your surgeon sterilizes the world where the hair will be removed and numbs it with an area anesthetic. You can also request sedation to remain asleep for the procedure.
Your surgeon then performs one among two transplant methods: FUT or FUE.
Follicular unit transplantation (FUT)
FUT is usually referred to as follicular unit strip surgery (FUSS). To perform a FUT procedure, your surgeon follows these steps:
Using a scalpel, the surgeon removes a bit of your scalp, usually from the rear of your head. The strip size is usually about 6 to 10 inches long but can stretch from ear to ear.
They close the world where the scalp was removed with stitches.
Your surgeon and their assistants separate the scalp strip into smaller pieces with a scalpel. They may split the work up into as many as 2,000 smaller fragments, called grafts. Some of these grafts may contain only one hair each.
Using a needle or blade, the surgeon makes small holes in your scalp where the hair will be transplanted.
The surgeon inserts hairs from the removed piece of scalp into the puncture holes. This step is called grafting.
They then cover the surgical sites with bandages or gauze.
The specific number of grafts you receive depends on the:
type of hair you have
size of transplant site
quality (including thickness) of hair
hair colour
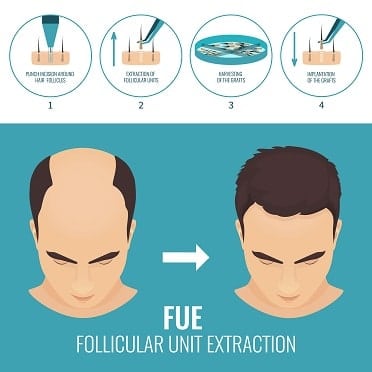
Follicular unit extraction (FUE)
To perform an FUE procedure, your surgeon takes these steps:
They shave off the hair on the back of your head.
The surgeon then takes the individual follicles out of the scalp skin. You'll see tiny marks where each strand was removed.
As with the FUT procedure, the surgeon makes small holes in your scalp and grafts hair follicles into the holes.
They then cover the surgical site with bandages or gauze.
Recovery
FUT and FUE may each take several hours to many days to finish. In part, this relies on the quantity of labour performed by the surgeon. You will go home the same day of the procedure.
Once the surgery is completed, your surgeon carefully removes any bandages. The area could also be swollen, so your surgeon might inject triamcinolone into the world to stay the swelling down.
You'll likely feel pain or soreness at the transplant site also as within the area where hair was taken from. For the subsequent few days,
your surgeon may prescribe:
pain medications, such as ibuprofen (Advil)
antibiotics to prevent infections
anti-inflammatories, like an oral steroid, to alleviate swelling
medications like finasteride (Propecia) or minoxidil (Rogaine) to assist stimulate hair growth
Here are some aftercare tips for hair transplant surgery:
Wait a couple of days after the surgery to scrub your hair. Only use mild shampoos for the primary few weeks.
You should be ready to return to figure or normal activities in about 3 days.
Don't press a brush or comb down over the new grafts for about 3 weeks.
Please don't wear any hats or pullover shirts and jackets until your doctor says it's OK.
Don't exercise for about a week.
Don't worry if some hairs fall out. This is part of the process. The transplanted hair might not grow much or seamlessly match the hair around it for a couple of months.
Hair transplant side effects
The most common side effect is scarring, and this can't be avoided with any procedure.
Other potential side effects include:
infections
crust or pus drainage around the surgical sites
scalp pain, itching, and swelling
inflammation of hair follicles (folliculitis)
bleeding
losing sensation around the surgical sites
visible areas of hair that do not match the encompassing hair or are noticeably thinner
continuing to lose hair if your hair remains balding
Minoxidil and Propecia also can have side effects, such as:
irritated scalp
dizziness
chest pain
headaches
irregular heart rate
hand, foot, or breast swelling



Comments
Post a Comment